Investigation on the role of Aperture Wall Thickness for the Generation of Sheet Electron Beam using COMSOL Multiphysics®
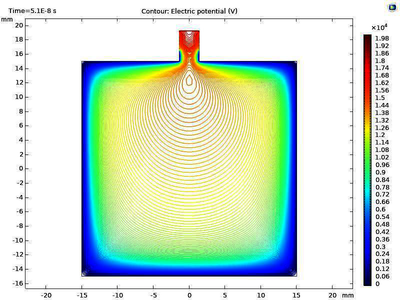
Pseudospark (PS) discharge is a low pressure hollow cathode discharge for generation of high intensity and high current density electron beams [1-3]. As the frequency of the microwave devices increases, the dimensions of the beam-wave interaction region gets reduced. In THz frequencies, the dimensions are in sub millimeter ranges for which high current density electron beam is required. This makes the PS based electron beam source most promising for the THz radiation sources [4,5]. For the designed planner interaction structure, the sheet beam is required for the maximum beam-wave interaction [6]. In this study, the role of the hollow cathode aperture wall thickness for PS based high current density sheet electron beam has been reported. A study using the COMSOL Multiphysics® software has been carried out to analyze the discharge variation in accordance with change in aperture wall thickness for the generation of sheet electron beam. The gas pressure and aspect ratio of the beam were kept constant. In sheet aperture, aspect ratio of beam is defined as the ratio of length to width of the aperture. The thickness of the hollow cathode aperture wall plays a very important role in the discharge density inside the hollow cathode and hence on the generation of the electron beam.
In the present study, a 2D hollow cathode geometry have been modeled with different aperture wall thickness in COMSOL®. The present work is carried out using the plasma module of COMSOL Multiphysics® for the simulation of the gas discharge in the hollow cathode and for the realization of electron beam generation. Electric field penetration inside the hollow cathode plays a very important role in the transit behavior of the discharge and hence the current of the E-beam. A simulation study has been performed for different wall thickness ranging from 1.05mm to 3.65mm keeping all other parameters like voltage, aspect ratio etc., constant. It is observed that with increase in wall thickness the field penetration inside the hollow cathode decreases, which cause the delay in the hollow cathode phase of the PS discharge. It has been analyzed that with increase in aperture wall thickness the duration of the hollow cathode phase increase. It has also been observed that the current, due to generated electron beam, decreases with the increase in aperture wall thickness.