- Bridging the Terahertz Gap
- Modeling the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Protection contre la Corrosion
- Modélisation des batteries
- Modélisation et Simulation dans le développement des piles à combustible
- Modélisation thermique des petits satellites
- Analyse électro-vibroacoustique d'un transducteur à armature équilibrée
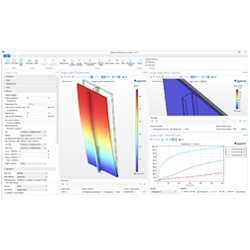
Gyproc Fire Resistance Analyzer – A COMSOL® App for Evaluating Gypsum Wall Systems
Fire resistance tests of building elements are essential for evaluating their ability to withstand fire exposure and prevent fire spread. Fire resistance tests are expensive and usually take months to organize. If the same structure is retested at the same lab, the systems are so complex that there is a risk of variation in the results due to details beyond the control of the project managers.
To address this, a numerical model for non-load bearing fire resistance tests, performed according to the EN 1364-1 standard, has been developed by Gyproc, a lightweight system producer within the Saint-Gobain group, and Deflexional AB, a certified COMSOL consultant. The model aids in understanding the mechanisms involved, improving existing systems, and designing new ones. The need for good computational tools is significant because extracting details of the construction for small-scale testing is challenging. This is due to the large-scale mechanics, such as bending of the entire structure and the macro effects of the board shrinkage, which are influencing the behavior.
The model is implemented in COMSOL Multiphysics® using the Heat Transfer Module and the Structural Mechanics Module. To enhance accessibility and expedite the modeling setup process, a simulation application has been developed to support all stages of the workflow. Utilizing COMSOL Compiler™, the application is converted into a standalone executable.
The app has two sub-models to evaluate the material parameters of gypsum boards. The first sub-model tests the insulation properties of the gypsum boards and allows users to choose parameters that match specific gypsum boards. The focus is on adjusting the temperature-dependent heat capacity to align with experimental data. This is important and a great simplification of the real process. Approximately 20% of gypsum boards consists of chemically bound water that evaporates when heated, maintaining the temperature around 100 degrees Celsius for an extended period. The second sub-model measures the thermal shrinkage of the gypsum boards based on experimental data.
The final part of the app is a thermo-mechanical model for full-scale EN 1364-1 tests, with adjustable geometry to accommodate the most common gypsum wall constructions. The model includes temperature-dependent properties for the steel studs and the gypsum boards. There is still potential for improvement, particularly in modeling the connection between the studs and the gypsum boards. The app offers many post-processing options, showing displacements, stresses, temperature, and material properties over time. Additionally, the app features an export option to make validation against experimental data from full-scale fire resistance tests easier.
The application thus enables a fast evaluation of the fire resistance performance of gypsum wall systems, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming physical tests. It also facilitates the optimization and innovation of new wall systems that meet fire safety requirements and customer needs.
Téléchargement
- ericsson_9451_poster.pdf - 1.64MB
