- Bridging the Terahertz Gap
- Modeling the Lithium-Ion Battery
- Protection contre la Corrosion
- Modélisation des batteries
- Modélisation et Simulation dans le développement des piles à combustible
- Modélisation thermique des petits satellites
- Analyse électro-vibroacoustique d'un transducteur à armature équilibrée
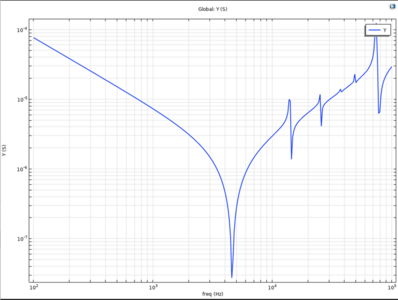
Sweep Frequency Response Analysis of Voltage Transformer for Medium Voltage Applications
In the medium voltage distribution network, voltage transformers play unique and critical role to monitor the power line voltage and thus controlling the flow and distribution of the electrical energy in the grid. During their service time, the voltage transformers are relatively often exposed to transient overvoltage events, power surges, switching and harmonics frequencies. Due to inherent construction of voltage transformers, they offer varying impedance of their primary winding, dependent on higher harmonics content in the power line voltage, which can lead to excessive currents causing thermal failure of a transformer. This paper presents a computational approach to characterize the impedance of the voltage transformers as a function of frequency in the medium voltage distribution networks and evaluate a potential risk of higher harmonics induced inner resonant overvoltage, The study utilizes a 2D finite element model of a voltage transformer developed in COMSOL Multiphysics (AC/DC Module). The model simplifies the transformer high voltage winding by grouping conductors which enables faster simulations while maintaining accurate and reliable results. Key winding parameters used in the computational model are carefully matched to a real-world object. By simulating the transformer's response across a frequency range, the model calculates the admittance, and subsequently impedance, of the transformer primary winding. The resulting frequency response is compared to a set of measurements obtained using Sweep Frequency Response Analysis (SFRA), a common technique for transformer health assessment. The paper provides valuable insights into the resonance behavior of a selected medium voltage instrument transformer, identified as the specific Y-axis points in the frequency-impedance plot. The discussed simulation method offers a valuable tool for detailed understanding and optimization of the voltage transformers performance in the medium voltage networks. The winding parameters like interlayer insulation, gap between the conductors, number of conductors in one-layer, total winding dimensions, etc. are defined to exactly represent a real object under the investigation. With frequency variation, admittance of the voltage transformer is calculated, and the resonance frequencies of the voltage transformer are found in the entire frequency spectrum.