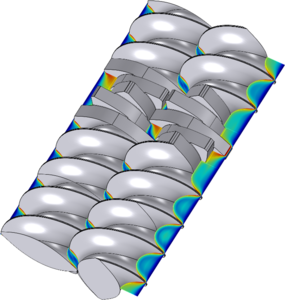
Numerical Simulation of Mixing with Intermeshing Rotors
Mixing processes driven by rotating machinery are common in many engineering applications, and the simulation of such processes can aid in understanding and optimizing the mass, momentum, and energy transport in these systems. COMSOL Multiphysics® contains built-in functionality for rotating domains with sliding meshes that can be used to simulate any number of rotating parts, but this built-in approach cannot be used for systems where multiple rotors occupy the same points in space at different points in time. For systems with intermeshing rotors, such as the twin screw extruder modeled in this work, an alternative method is required. A new technique for simulating transport processes driven by intermeshing rotors has been developed in this work and applied to 2D and 3D models, with the ultimate goal of predicting heat generation due to viscous dissipation in a food extruder.