Hydrodynamic Performance and Stability Characteristics of heavy Oil-Water Annular Flow
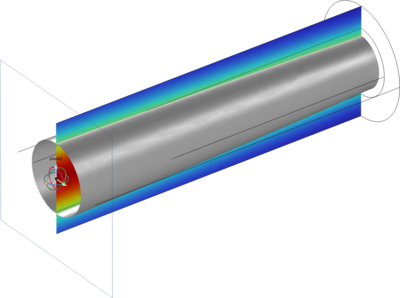
The transportation of highly viscous oil surrounded by water annulus can be a practical option in terms of low-energy consumption and high efficiency. The stability of maintaining this type of flow can be challenging, especially with highly viscous oil. In this present study, three-dimensional numerical simulations for oil-water core annular flow (CAF) through 1” horizontal pipe were performed using COMputational SOLution (COMSOL) based on the two-phase level set method (LSM). Simulation results were consistent with experimental data, which verifies the validity and practicality of the proposed model. The effects of inlet water fraction, liquid holdup, superficial velocities of oil and water, oil properties (density and viscosity), and oil core related parameters (size and position) on the hydrodynamic performance and stability characteristics were explored. It is revealed that inlet water fraction, superficial velocities of oil and water, oil properties, and oil core geometric parameters influence the volume fraction of oil and the stability of the water ring. The results could provide a reference for flow assurance in pipe structures and optimization of operation parameters.
Téléchargement
- alawadi_9231_poster.pdf - 0.6MB
