Tubular Centrifuge
Application ID: 127971
A tubular centrifuge is a type of centrifugal separation device that is often used for separation of very fine solid particles from a liquid. It can be run in both a continuous and batch type configurations. The device usually consists of a cylindrical rotating bowl with a large aspect ratio where its length is often many times larger than the radius. The bowl has an inlet feed and an outlet.
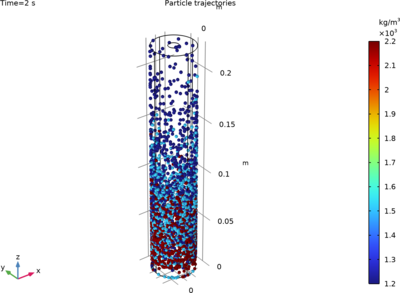
The particle–liquid mixture enters the rotating bowl through the inlet feed. The large rotation speed of the bowl induces centrifugal forces on the particles which cause them to sediment near the inner walls of the bowl as long as the particle has a larger density compared to the fluid. The sedimentation rate depends on the particle densities and the rotation speeds. Larger rotation speeds enhance the sedimentation rate. Further, the particles with larger densities tend to sediment faster. This dependence on the particle densities can lead to a preferential sedimentation along the axial direction with the most dense particles sedimenting close to the inlet, while the less dense particles sediment at a larger axial distance from the inlet.
This model also demonstrates the process of restarting particle tracing simulations whereby the information of the particles from one study step is used as the initial conditions for a subsequent study step.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Grille des Spécifications and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
