|
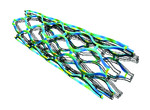
A stent is a wire-mesh tube used to prop open an artery during angioplasty. The stent is collapsed to a small diameter and put over a balloon catheter. It is then moved into the area of the blockage. When the balloon is inflated, it expands and deforms the stent to the desired size, holding the artery open. The stent stays in the artery permanently, holds it open, and improves blood flow to the heart muscle.
This model investigates the expansion of the stent taking into account its superelastic properties. Using the Structural Mechanics Module, the model investigates the von Mises yield criteria. Too little strain and the stent is not sufficiently flexible; too much strain and it does not maintain its functional shape.
|

